Recently, the decree amending the Regulation respecting wastewater disposal and treatment systems for isolated residences came into force, thereby allowing the installation of an on-soil cabinet under certain conditions. It is now open to anyone to set up a composting cabinet for the treatment of sanitary wastewater following certain conditions prescribed in the regulations. What exactly is the compost cabinet better known as a compost toilet?
- How does a compost toilet work?
- What technologies are available for composting toilets?
- What uses can be made of this compost toilet?
Composting is a natural biochemical process allowing the decomposition of organic matter by aerobic microorganisms. These microorganisms use the oxygen in the air to degrade the carbon sources in organic waste to convert it into CO2, water, and energy (heat). The result is a stable, mineralized residue free of pathogenic organisms – compost.
The compost toilet uses the same process in a controlled environment: the compost chamber.
The microorganisms found in the compost bin are mainly bacteria, actinomyces, fungi, invertebrate organisms (arthropods) and various varieties of microbial worms. This diversity of microorganisms is obviously not found in the intestinal flora, hence the obligation to manually sow selected cultures allowing the composting process to begin.
To maintain the optimum temperature, a circulation of preheated air is maintained through the decomposing residues, supplying oxygen to the microorganisms. A liquid recirculation system keeps the proper moisture content in the compost to support microbial activity.
A stand-alone vent, usually coupled to a mechanical turbine, allows odors and digestion gases to be removed while bringing fresh air into the composting chamber.
What technologies are available for composting toilets?
To be installed, the compost toilet must necessarily be certified by the relevant organizations of each country and comply with their standards. Some companies holding these certifications use different processes for transforming dejecta into compost.
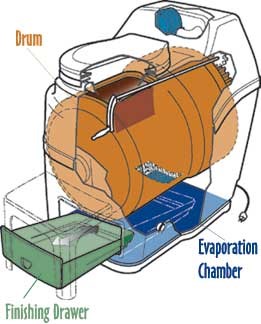
* 3-chamber technology (composting, evaporation and finishing drawer) developed by Sun-Mar company
The composting chamber uses the rotary drum principle. Called Bio-Drum, the manual tumbling of the drum optimizes the mixing and aeration of the compost while maintaining a uniform moisture content and oxygenation. The Bio-Drum allows evacuating the excess moisture contained in the compost by draining the excess liquid to an evaporation chamber.
The evaporation chamber has a large evaporation surface with a thermostatically-controlled heating element. This heating surface promotes the evaporation of excess liquid accumulating in the evaporation chamber, and the generated vapour passes through the compost to keep it moist.
The finishing drawer:
This is an insulated chamber, located at the base of the unit, into which the compost falls when the Bio-Drum is turned in the opposite direction. Once in the drawer, the compost can remain there to complete the composting process. In this drawer, the compost is subjected to a current of air that allows it to dry gradually before being removed.
This sloping design allows for the separation of liquids from urine and faeces. When urine percolates by gravity through the compost to the low point of the composting chamber, the bacterial activity causes the biochemical transformation of specific components of the urine (urea and ammonia) into a liquid rich in nitrate and nitrite. Some of this liquid is sprinkled on the compost to maintain adequate moisture content to support bacterial activity. Excess leachate should be discharged to a fully drained pit.
This separation also ensures that the compost is not saturated with liquid and maintains aerobic conditions. The microorganisms in the composting chamber degrade and convert the material into chemically and biologically stable compost.
The composting process reduces the volume of dejecta fed into the composting chamber by more than 90%.
This composting chamber is also equipped with a mechanical ventilation system allowing the evacuation of digestion gases and water vapour while supplying the composting chamber with fresh air for the oxygenation of the environment.
What uses can be made of this compost toilet?
The management of the compost obtained from a compost toilet must be done under regulations:
* Recycled by spreading on the ground per the Guide to the Recycling of Fertilizer Residual Materials;
* Valued if the municipality accepts the residues from the compost bin;
* Disposed of via garbage collection (sanitary landfill site authorized by the municipality.)
If you want to see more useful information about different categories, please visit our website.











