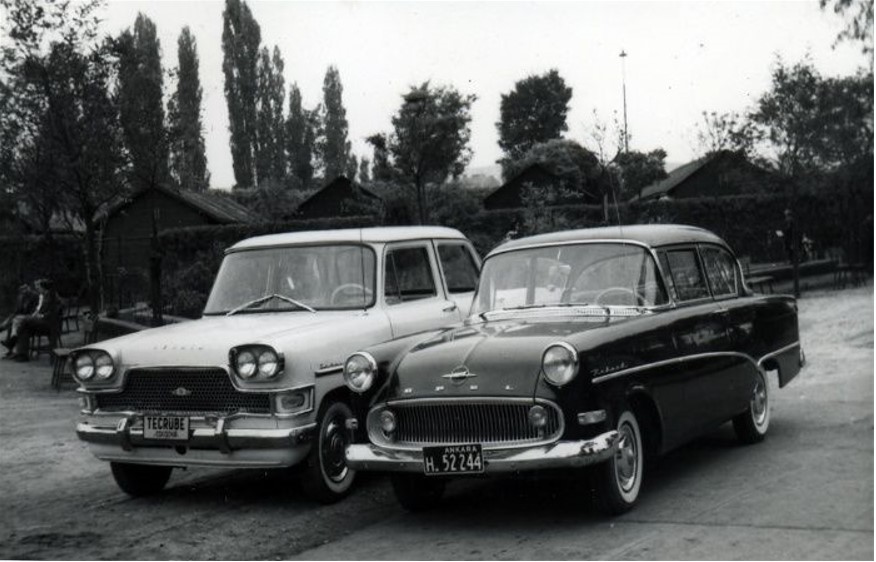
The importance of automotive industry in Turkey comes first whenever it’s mentioned to the country’s economic and industrial developments. The automotive industry has a cornerstone value for industrialized countries. It is due to a large number of buyers in different business areas. For example, the automotive industry is a buyer in many industries. These are such as iron and steel, automotive supply, and tire industries. Apart from this, it generally provides services to various sectors that require a motor vehicle workforce; we can exemplify these services with tourism, construction, agriculture, transportation, and many others. Therefore, changes in this sector greatly affect the economy.
Today, approximately 20 companies can’t dominate just %10 of the automotive industry in the world, and the remaining part belongs entirely to these 20 companies. The automotive sector is of great importance for Turkey with its tax revenues, contribution to employment. Moreover, the added value it creates, and its contribution to many industries are other examples of its importance. This article will examine the automotive industry in terms of its coverage areas, its beginning in Turkey, and its spatial distribution throughout Turkey with the factory numbers and brands.
-
What production and employment areas does the automotive sector cover?
-
Beginning of the automotive sector in Turkey
-
Spatial distribution of factories
-
How many factories are there?
What Production and Employment Areas Does the Automotive Sector Cover?
The automotive industry is one that manufactures motor vehicles. Automobile production is significantly higher than that of other motor vehicles. Automobile production, in this sense, develops a robust sub-industry and supports the production of additional vehicles. As a result, automobile production is the backbone of the automotive sector. The automotive industry is the primary buyer of basic industry products such as iron and steel, light metals, petro-chemistry, rubber, and plastic. For further it is a sector that forces and contributes to the technological development of these sectors in perfect sync with the technological developments in the automotive sector.
The automotive sector listed the marketing, dealer, service, fuel, finance, and insurance sectors as a significant business volume and employment by itself. These sectors enable and support the delivery of raw materials, sub-industry, and automotive products to the consumer. Especially in Turkey, the automotive sector provides employment to areas in factories that manufacture, companies selling second-hand cars, or new cars. It also provides employment to car rental companies, auto repair, auto spare parts. Additionally online automotive sales, online auto spare parts sales, appraisal, traffic insurance, and motor insurance companies are among these employment facilitates.
Beginning of the Automotive Sector in Turkey
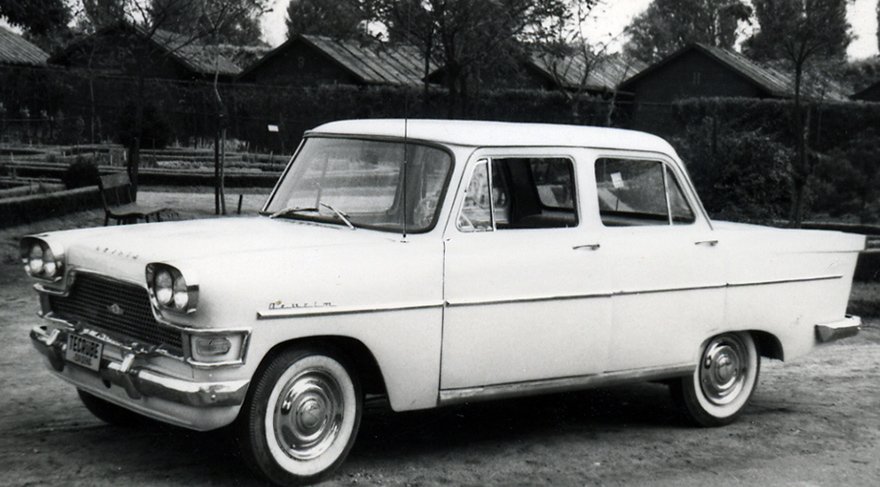

The Turkish automobile industry began in 1954, with the establishment of a Jeep factory in Tuzla. The goal of establishing this factory is to build military vehicles for the Turkish Land Forces rather than passenger automobiles.
Meanwhile, this factory also began to produce trucks in the following years. Yet, later the State Railways factory in Eskişehir, with extremely restricted facilities conducted the initial steps for automotive manufacturing. These were in line with the directive of the President of that time, Cemal Gürsel. In 135 days, four cars were manufactured. These four-door sedans with lengthy chassis were dubbed as “Devrim”. However, owing to period opportunities, internal issues, and other unknown problems, these automobiles did not go to the mass production line. After a small break, Turkish citizens manufactured the indigenous vehicle “Anadol”12 years after the Ministry of Industry authorized the concept in 1966. They created a Turkish automotive factory in 1968 as a result of this achievement. This factory manufactured Murat 124 model cars.
Given the fact that Turkey’s automobile sector was steadily growing, they built several new factories during the next 10 years. In the 1970s, facilities for BMC, Crysler, Karsan, and people established other comparable brands. Then the mass manufacturing began. In addition to this, the spare parts business has demonstrated significant growth in a sector that has demonstrated success. During the same time period, engine components, pistons, tires, and a variety of other spare parts were made in Turkey. For further, vans were built to deliver these parts. Since the mid-1980s, companies like TOYOTA, HONDA, and RENAULT have constructed facilities and begun manufacturing here. These companies appeal more to the world of average-income families.
Spatial Distribution of Factories
When motor vehicle manufacturing in Turkey was based on assembly (1955-1970), the majority of the production operations were carried out in Istanbul. The automobile industry operations began in Bursa in the 1970s. It moved inland in the 1980s (Aksaray, Eskişehir, Ankara, Adana), and primarily in Kocaeli and Sakarya in the 1990s. On one hand, the Marmara Region is the region in Turkey with the highest concentration of automotive main industry operations. On the other hand, Bursa is at the forefront of the cities in this region with the highest proportion of automotive main industry activities. According to a report by DergiPark, the map below provides a quick glimpse of the spatial distribution of automotive factories:
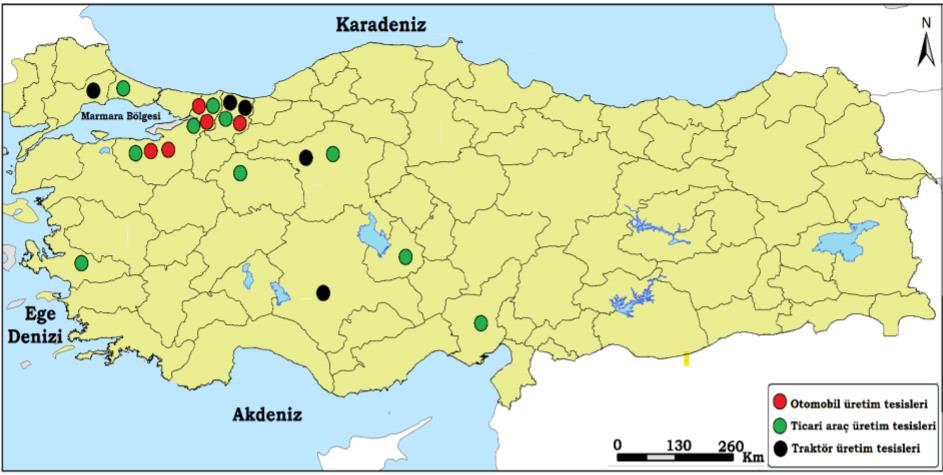
Strong brands such as Karsan 1966, Tofaş 1971, and Oyak-Renault 1971 have also chosen this region as the place of establishment. Brands like Hyundai Assan (1997) and Honda (1997), on the other side, chose Kocaeli as their establishment. Many other different companies such as Toyota, Otokar, Türk Traktör, Ford-Otosan truck factory 1983, MAN truck factory 1985, Mercedes Benz Türk truck factory 1986, Tümosan and Erkunt have taken their place in the Turkish market for motor vehicle production.











